Prime
Range of Pre-Laminated MDF Board
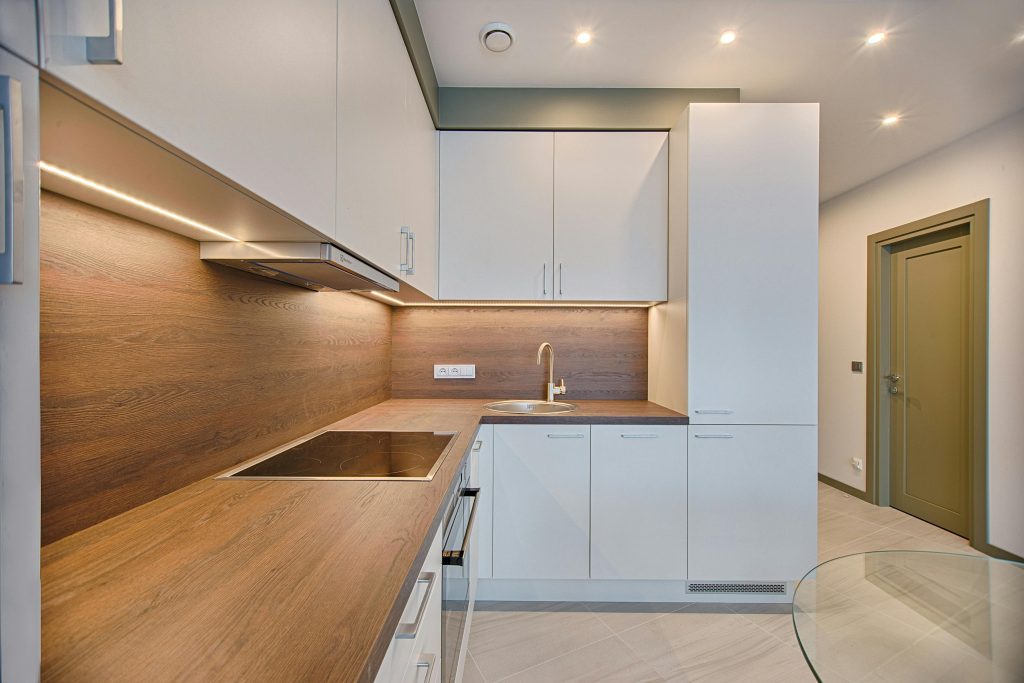
Discover PRIME, our premium Pre-Laminated MDF boards that redefine durability and aesthetics. Crafted from wood fibers and synthetic resins, PRIME sets industry standards. Available in interior and exterior grades, these versatile boards elevate projects in furniture, interior design, retail, exhibitions, partitions, and modular kitchens. Experience innovation and unmatched performance with PRIME, the pinnacle of our product range.
PROPERTIES

Versatility
Available in diverse finishes, colors, textures, and patterns.

Durability
Resists damage, moisture, stains and is easy to maintain.

Machinability
Easy to cut, shape, customize.
Applications

exhibitions

interior design

retail

doors
Comparison Between MDF & Plywood Boards
When deciding between Medium Density Fiberboard (MDF) and Plywood boards, understanding their distinct characteristics is crucial for making an informed decision. This point-by-point comparison highlights why MDF is often considered superior to Plywood boards in various aspects. From its smooth surface to cost-effectiveness, MDF offers several advantages that make it an excellent choice for numerous applications. Let’s take you through a quick attribute-wise comparison between the two.
| ATTRIBUTES | MDF | PLYWOOD |
| Consistent Density | MDF’s even density throughout the board ensures consistent strength, eliminating weak spots or knots found in Plywood. | Plywood’s cross-laminated layers may lead to slight variations in density, potentially affecting performance in specific applications. |
| Smooth Surface | MDF boards offer a flawless and uniform surface, perfect for laminations, veneers, and painting, resulting in a seamless and polished finish. | Plywood’s natural wood grain appearance may not be as smooth, requiring additional preparation for a refined surface. |
| No Warping | MDF is less prone to warping or shrinking, making it reliable for large-scale projects and applications in humid environments. | Plywood may be more susceptible to warping if not appropriately treated for water resistance. |
| Cost-Effectivene | MDF is generally more affordable than Plywood, providing a cost-effective solution without compromising on quality. | Plywood’s cost can vary depending on the wood veneer used, making it potentially more expensive in some cases. |
| Environmental Impact | MDF is often made from recycled wood fibers, contributing to sustainability and eco-friendly practices. | While Plywood can be sourced sustainably, MDF’s recycled content enhances its environmental advantages. |
| Interior Applications | MDF’s smooth surface, consistency, and absence of voids or knots make it an excellent choice for interior applications like cabinetry and furniture. | Plywood’s strengths are better suited for structural and outdoor projects, making it more suitable for exterior use. |
| Composition | (MDF) is made of very fine wood fibers that are glued and compressed under great pressure | Plywood is made of thin sheets of wood that are laminated in alternating directions |
| Strength | Offers medium rigidity | Good at providing rigidity for structures |
| Screw holding capacity | Highly compressed, thus holds screws firmly | Stronger cross-grain pattern, that allows strong grip to screws and nails |
| Usage | MDF can be used for wardrobes, doors, media units, bunk beds, kitchen cabinets, shelving units,etc. | They absorb moisture easily, thus plywood is not fit for exterior usage |

Design & Shade catalogue